Environmental change
Daijiang Li
LSU
Announcements
Global Environmental Change
What are the problems?
What can we do about them?
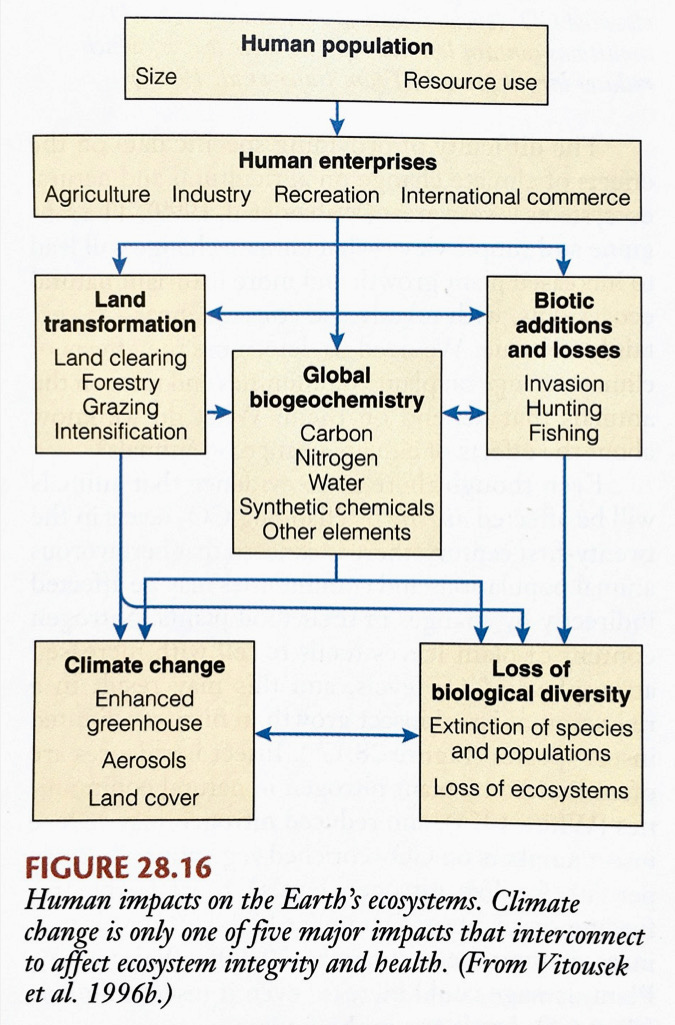
Throughout this course, we have touched on many environmental change problems, from land use change to pest control to species diversity loss. This lecture will bring these environmental change problems into central focus and we will briefly talk about what are the problems? and what can we do about them?
these issues are not separate from each other
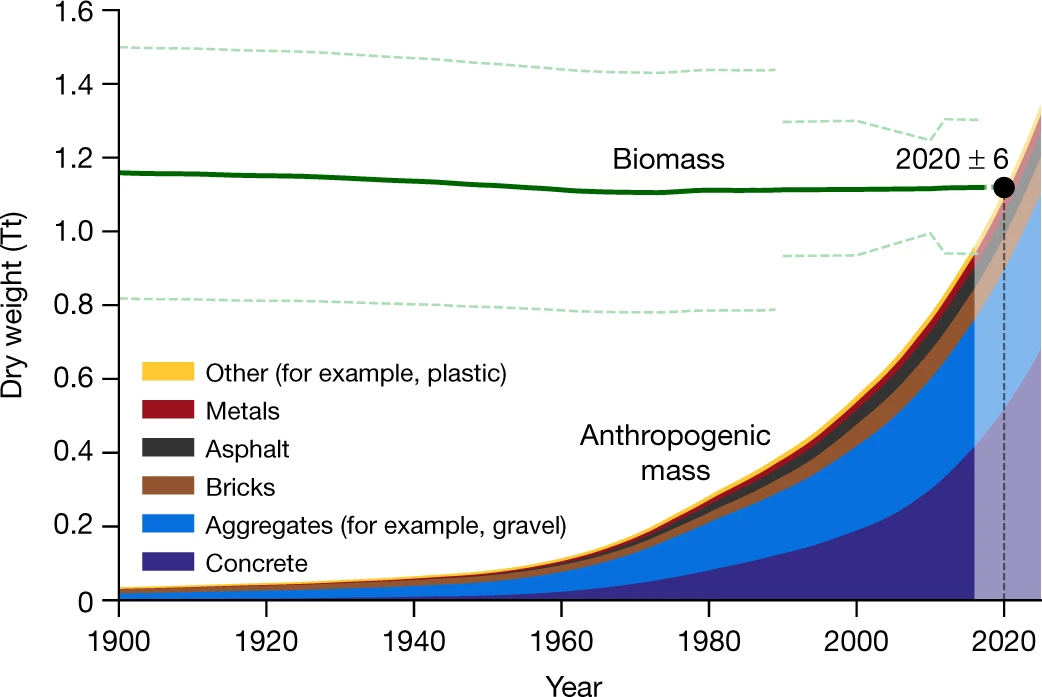
The total value of global ecosystem services is estimated to be ~125 trillion US dollars per year; while global gross domestic product (GPD) in 2012 is ~74 trillion $.
Human Population Growth

Beyond exponential; Carry capacity? https://ourworldindata.org/world-population-growth
10-12 billion
Welcome to the Anthropocene
The exponential growth of human population has led to increasing pressure on natural systems.
What are the problems?
Land use change
Biological invasions
Climate change
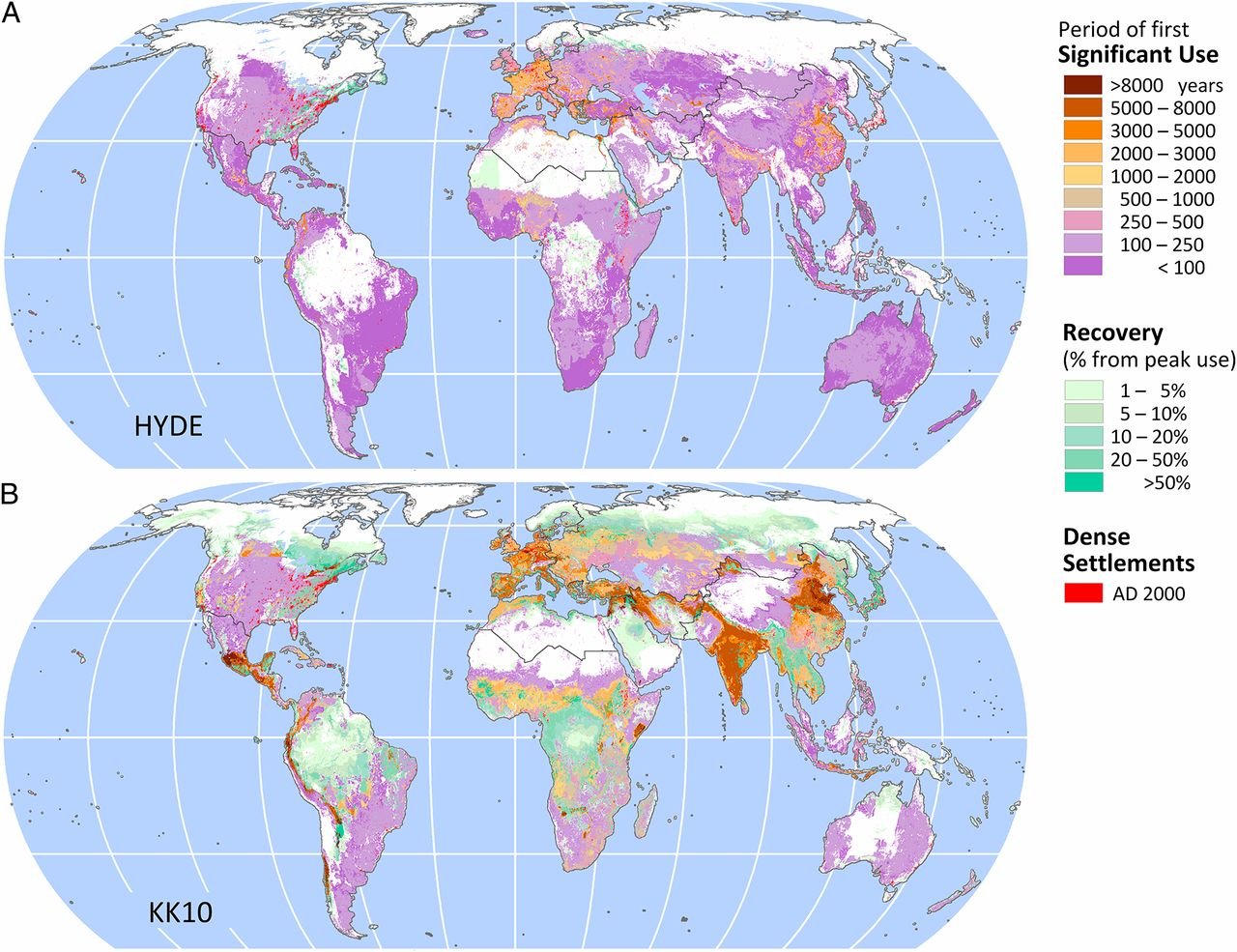
Land-use change
Agriculture and urbanization since thousands years ago; accelerated in the last several hundred years (Ellis et al. 2013)
gigatons = a biliion tons
Consequences of land-use change
Habitat lost for plant and animal
Habitat fragmentation and associated problems
Carbon emissions and consequences for climate change
Even activities without dramatic land clearing can have large-scale effects: e.g., irrigation, dams
Biological Invasions
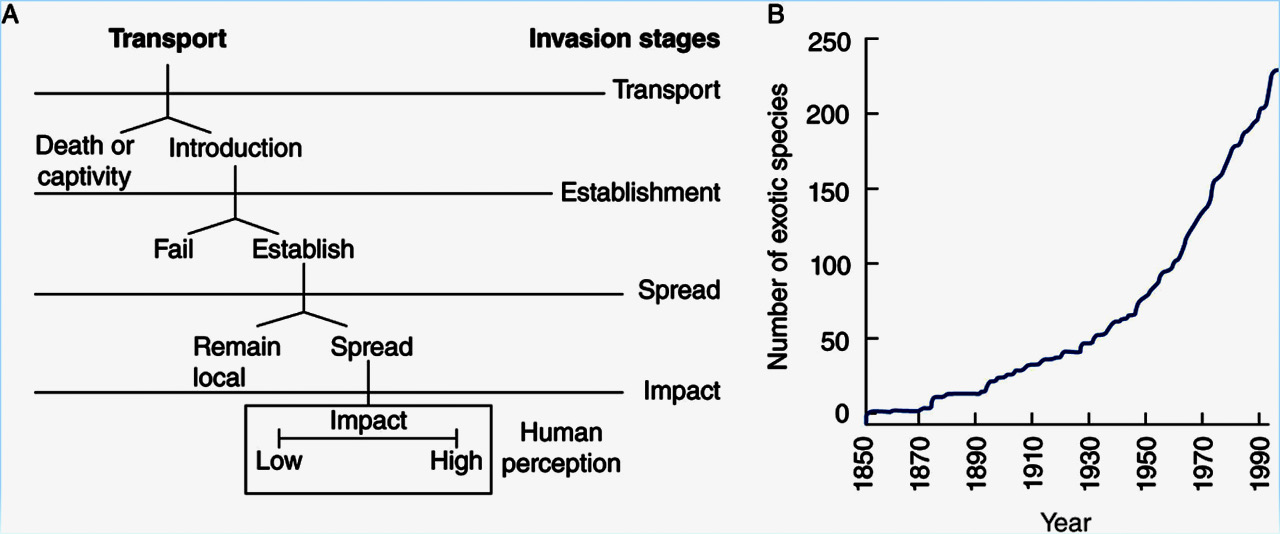
Large ecological impacts (as predators, competitors, disease vectors, pathogens, etc.); > 120 billion $ loss per year in US
e.g. fire ants
Hypothese of species invasions
The Carbon cycle
Atmospheric CO2 concentration
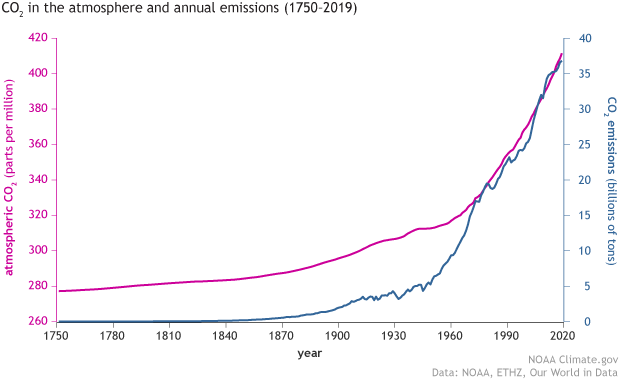
March 2021
417.64
parts per million (ppm)
Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii (Scripps UCSD)
March 2022
418.81
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
Greenhouse effect
Increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases (e.g., CO2 (81% emission), CH4 (10% emission, 80x CO2), N2O (7% emission, 300x CO2), chlorofluorocarbons CFCs (3% emission, 5000x CO2)) will warm the Earth
O3,
Global Warming Potentials https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/understanding-global-warming-potentials
Long-term association between CO2 and temperature

Long-term association between CO2 and temperature

Association is not causation
The main evidence for anthropogenic climate change is from Global Climate Models

Climate Change: a major environmental issues of our time
Global Climate Models: 4-11 °F by 2100 (10-100 times faster than natural)
5°F: hottest in 100,000 years
9°F: hottest in 1,000,000 years
Climate Change: a major environmental issues of our time
Global Climate Models: 4-11 °F by 2100 (10-100 times faster than natural)
5°F: hottest in 100,000 years
9°F: hottest in 1,000,000 years
Cold regions will get hotter
Dry regions will get drier
Some impacts of climate change
- Sea levels will rise
- Hurricanes will increase
- Extreme weather will be more frequent
- Fire regimes in the US West will change
- Increased CO2 will acidify oceans
- Species: adjust, adapt, move, die
- Changes in species interactions
- Plant growth and phenology will change
Sea level rise
Thermal expansion
Melting glaciers
Melting Greenland and Antarctica
Melting Glacial


Sea level rise
Thermal expansion
Melting glaciers
Melting Greenland and Antarctica
Current: 8 inches above 1880
2050: another 6-16 inches
2100: another 12-48 inches
Sea level will rise even after global temperatures stabilize
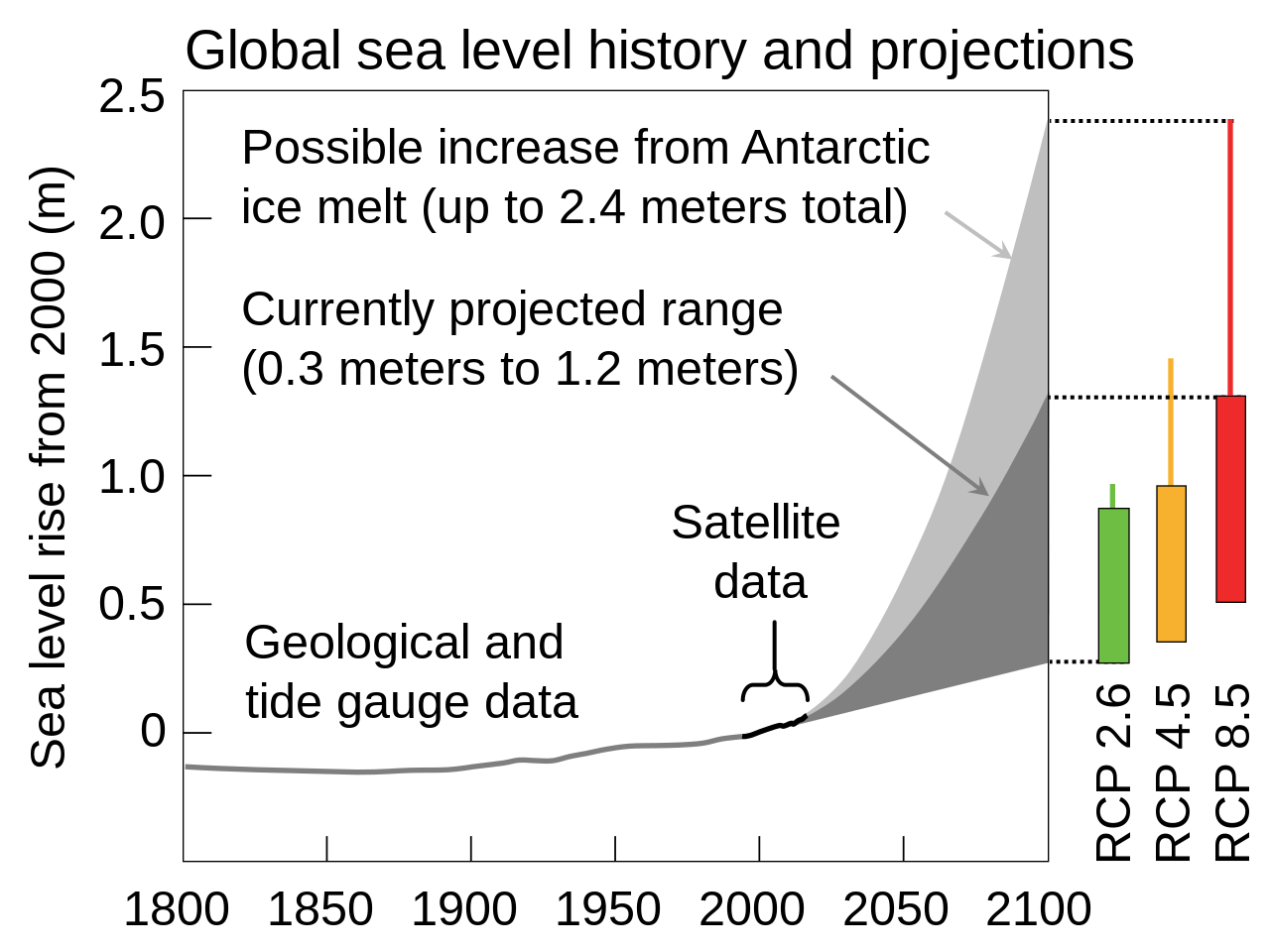
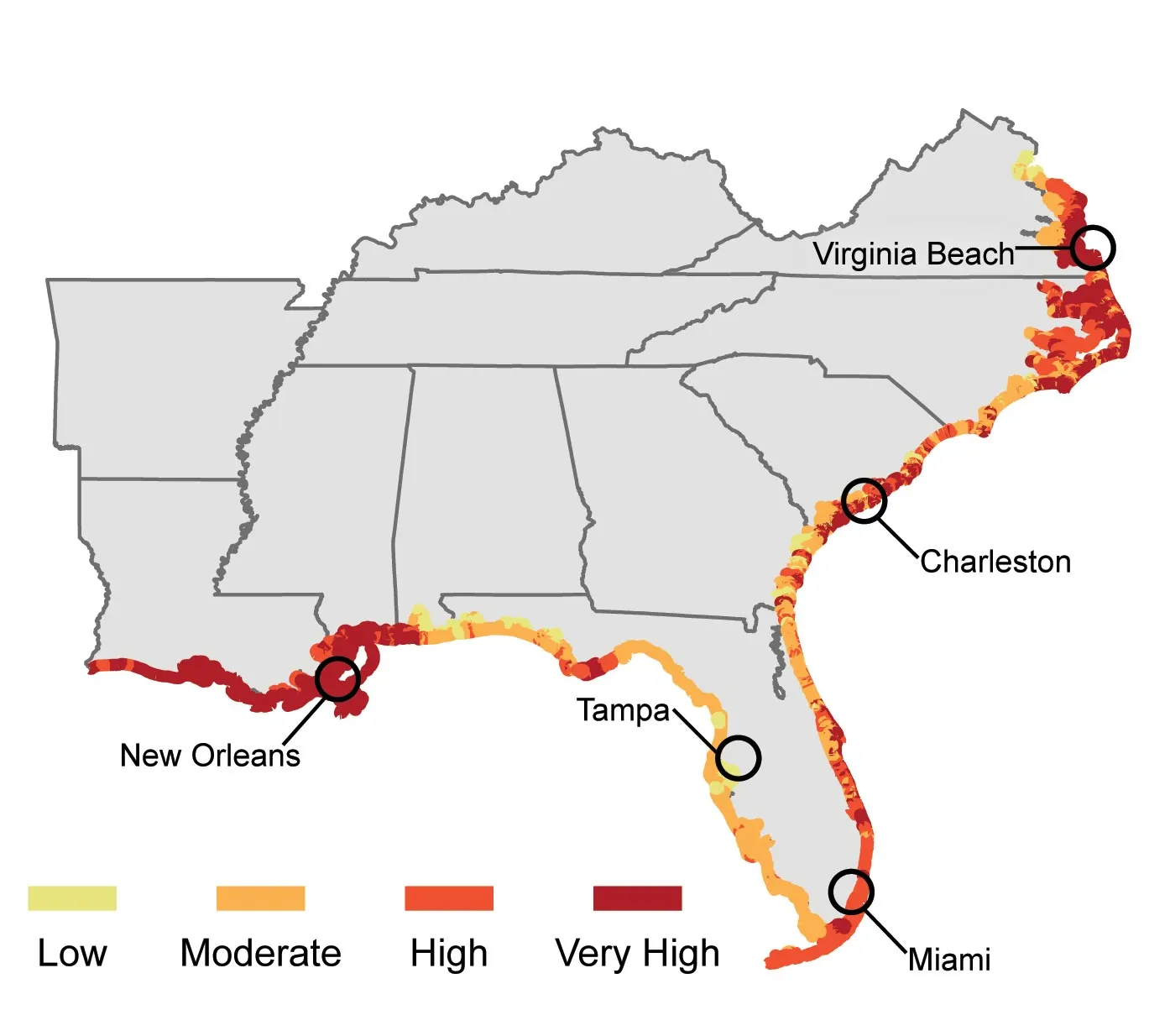
Hurricanes will increase
Hurricane Katrina in 2005 caused over 1800 deaths (~1200 from Louisiana) and $125 billion in damage.
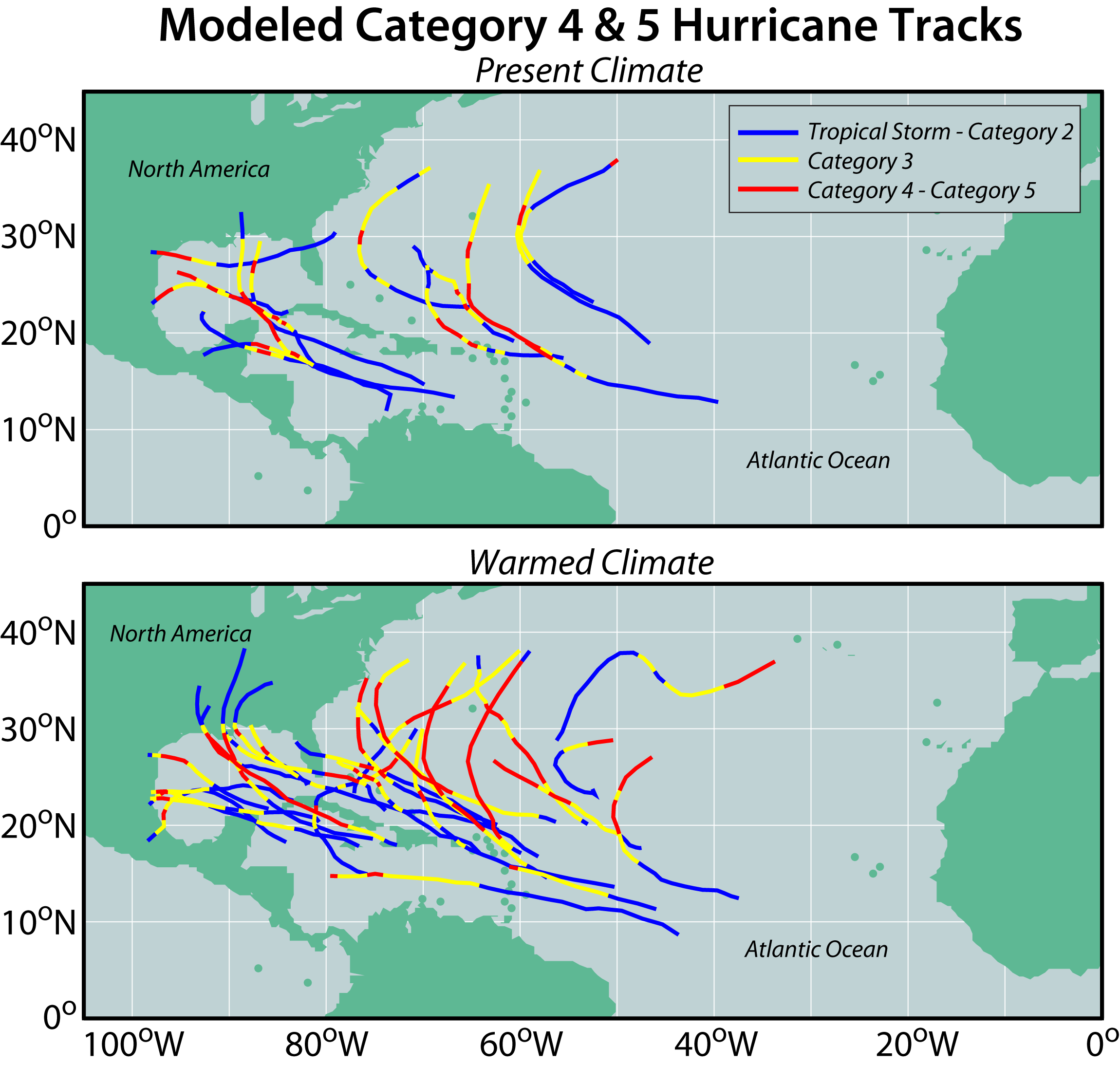
Storm intensities should increase as the latent heat of water vapor rises with air temperature
Extreme weather will be more frequent
Heatwavers, heavy rain and flooding, drought, and paradoxically, extreme cold
Climate change and record cold: What's behind the arctic extremes in Texas
Frozen Louisiana pic.twitter.com/RemKOtQMb6
— The duck girl (@Louisianaboater) February 16, 2021
a warmer climate may have actually contributed to the extreme cold
Fire regimes in the US West will change
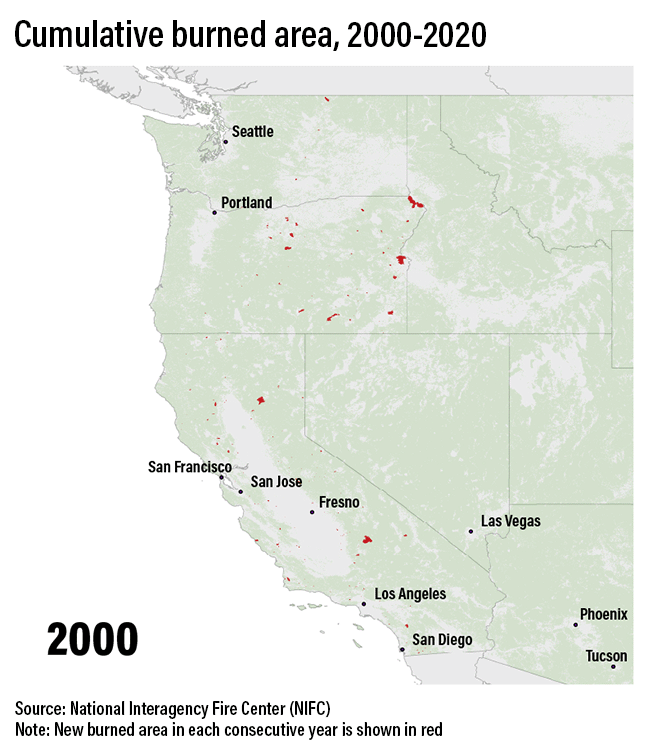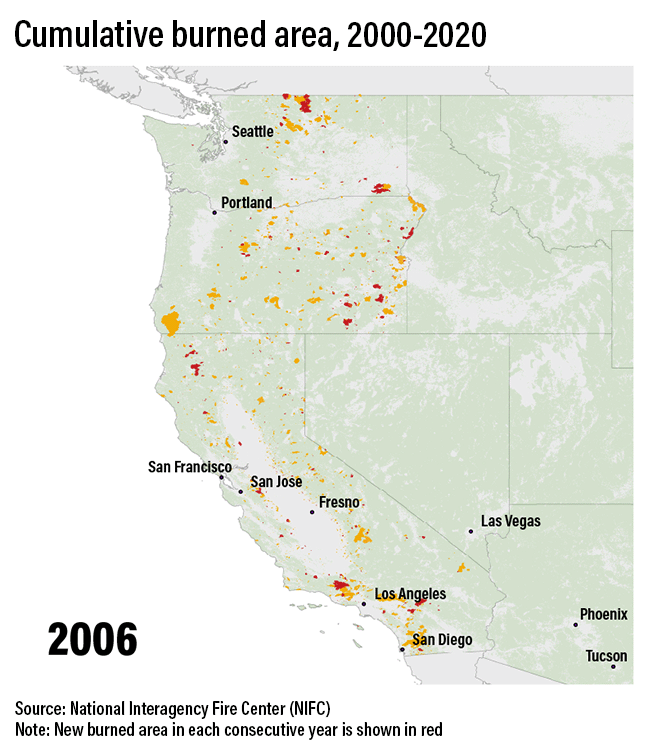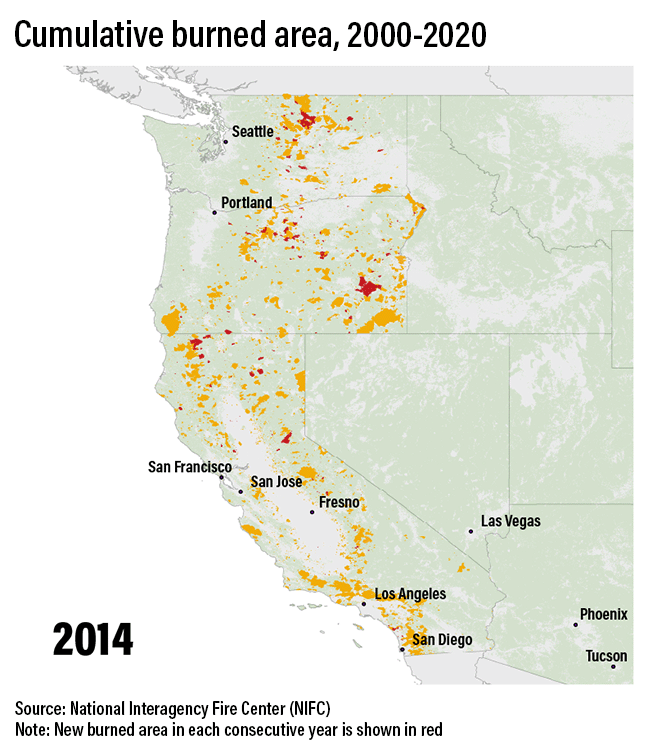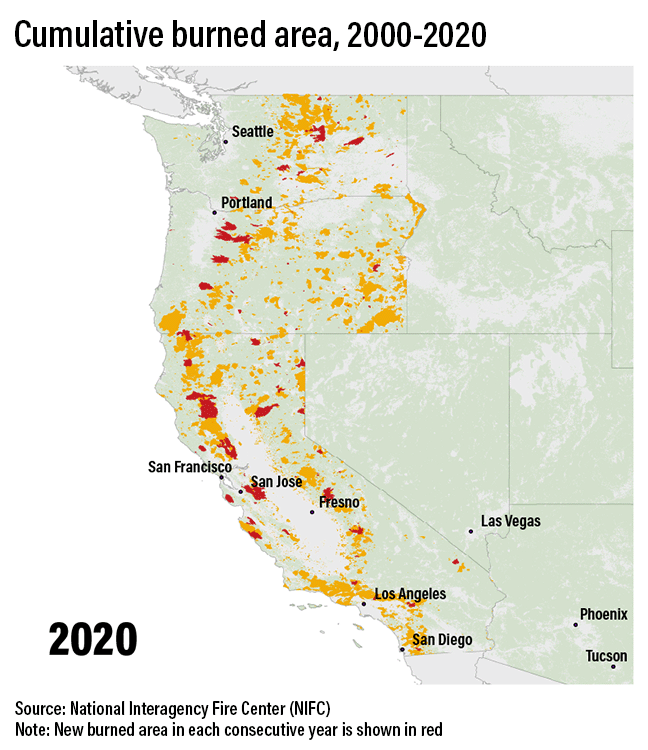
Fire regimes in the US West will change
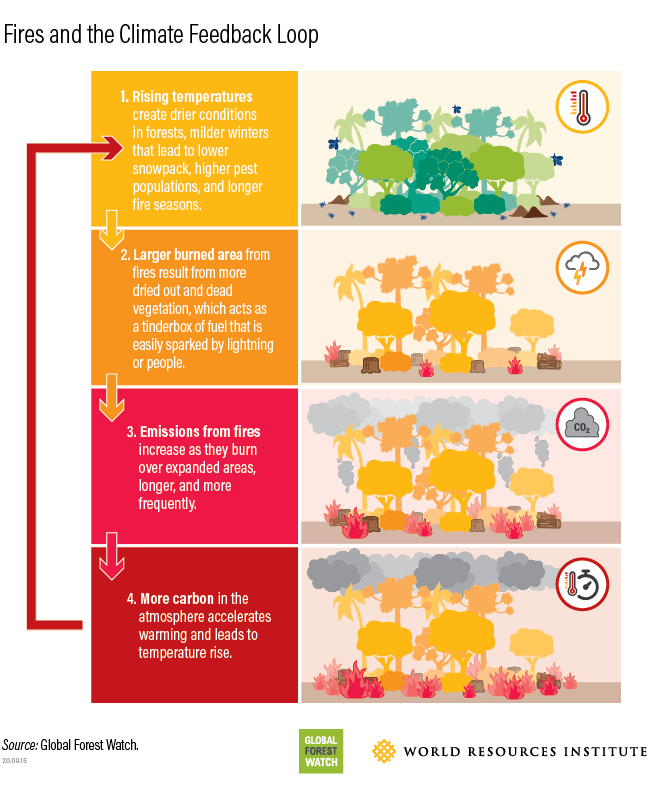
Higher temperatures draw moisture out of live and dead trees and brush, making them more flammable. The heat also can alter precipitation, as well as shift spring thaw earlier, lengthening the fire season.
Ocean Warming and Acidification
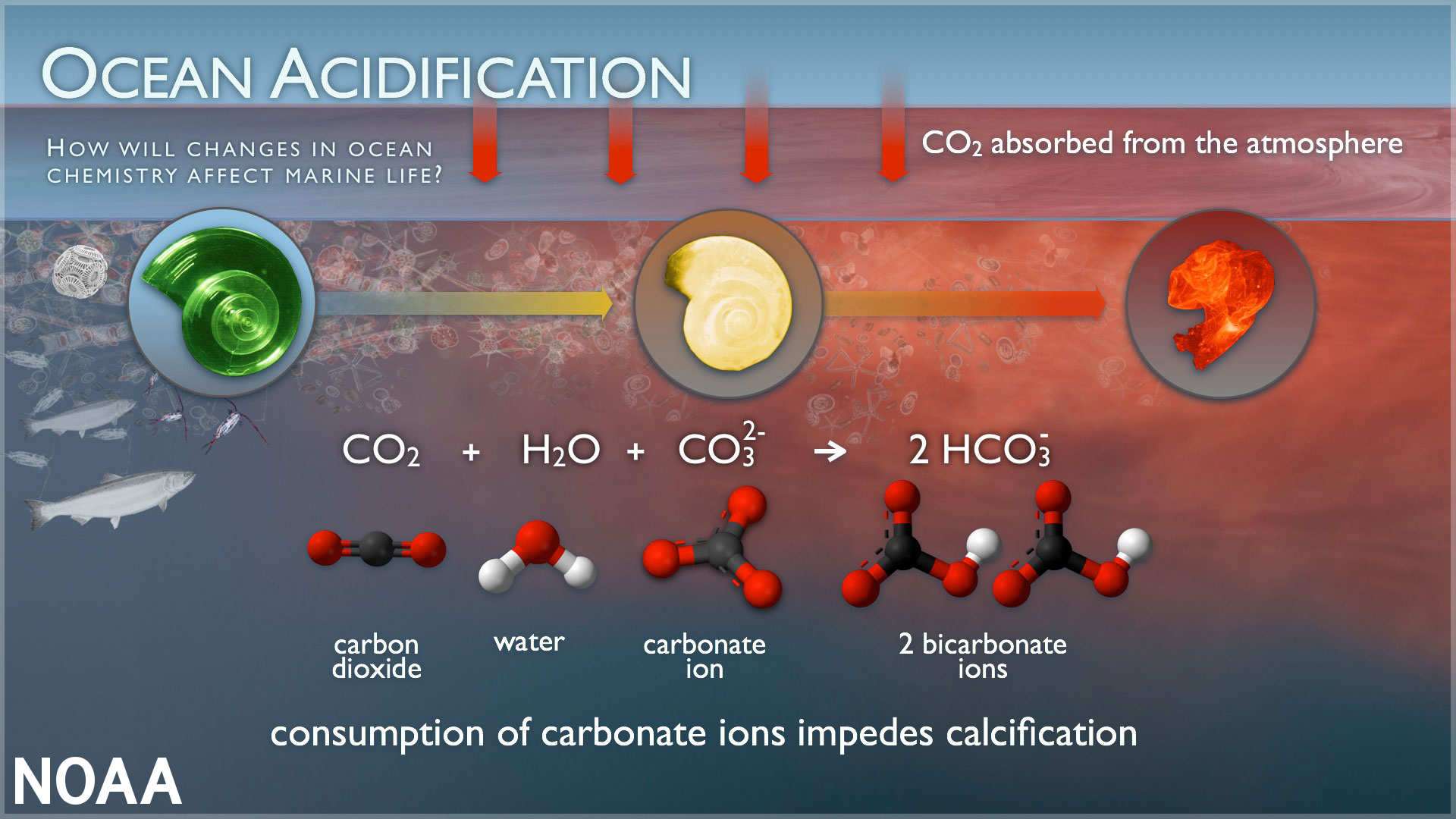
A problem for ocean ecosystems and commercial industries like oyster farms
less carbonate ions (co32-) to build shells
shells and skeletons can even begin to dissolve
Ocean Warming and Acidification
What is this??
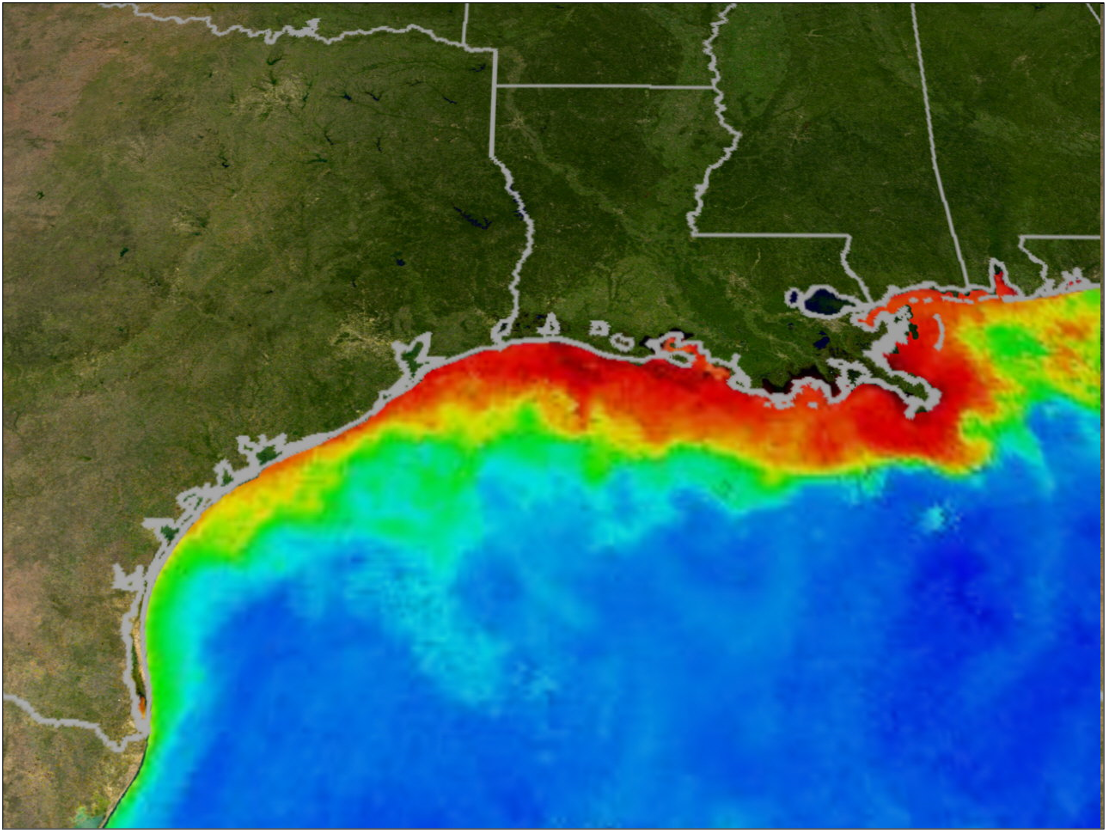
Spreading dead zones
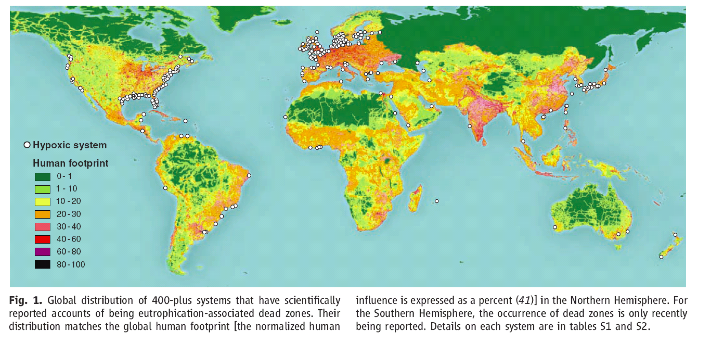
Diaz and Rosenberg, Science, 2008
Species: adjust, adapt, move, die
Adjust: changes that occur during an individual's lifetime, typically not passed down to offspring; sometimes referred to as acclimation, acclimatization, or plastic responses
Shifts in phenology

Plants and animals are flowering, mating, and migrating earlier (Root et al. 2001)
Species: adjust, adapt, move, die
Adapt: populations become better suited to environmental conditions they experience via heritable genetic change over generations
Adaption is necessary for species' long-term persistence as they struggle to survive in environmental change
Adaption by natural selection

Species: adjust, adapt, move, die
Move
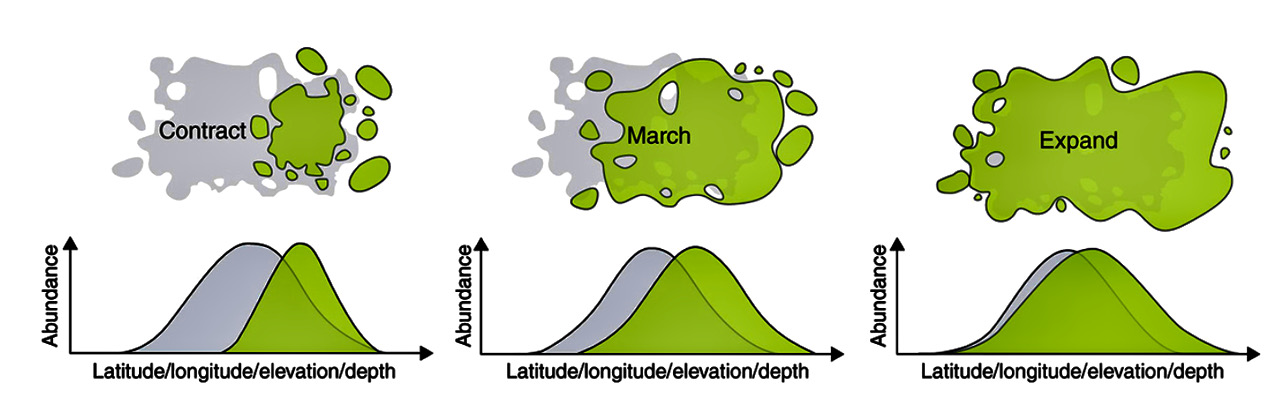
Species: adjust, adapt, move, die
Move
 Die: fail to adjust, adapt, or move; loss of individuals, populations, and species
Die: fail to adjust, adapt, or move; loss of individuals, populations, and species
Human-mediated extinction rates are accelerating: sixth mass extinction
Changes in species interactions
phenological mismatch, trophic mismatch, etc.
What can we do?
Waste less, eat less meat, drive less, fly less, buy less
What can we do?
Waste less, eat less meat, drive less, fly less, buy less
Don’t doubt the science
"It's clap-trap. Far too many people in the Government and media are far too willing to listen to and amplify any claim of doom by someone who's wearing a white coat."
-Rep. Dana Rohrabacher
Chairman of the House
Subcommittee on the
Environment, 1995
Human impacts on the planet's ecosystems are dramatic and growing. During our life time, these impacts will led to the most significant problems facing the global. One may feel angry about the past, hopeless about the future. But I think our huge impacts on environment also reveals our collective power and the large potential to make our future better. I think now is a fascinating time to be a scientist because never before we have had such significant and complex impacts on the ecosystems, while at the same time we also have powerful tools to solve issues and conserve life. Whether or not you pursue a career in Global Change Biology, I hope this lecture will help us to be more informed citizens. Together, we can make our future better and sustainable.